PreciseDx™
Multimodal Comprehensive Gene Profiling (CGP)
Personalized Cancer Care Through Unparalleled DNA & RNA Analysis
What if
we can accelerate treatment decision-making and reduce diagnostic expenses
One biopsy, one test, one report can lead to improved patient outcomes
Experience the power of precision oncology with the AGTC Genomics PreciseDx™ Multimodal Comprehensive Gene Profiling (CGP). Our comprehensive gene profiling tool delivers the power of one solution for simultaneous DNA and RNA analysis, providing a comprehensive view of genomic alterations and gene expression changes in cancer. With broad coverage of cancer types, this panel is designed to shorten the duration of treatment decision-making, empowering you to make informed and confident decisions for your patients. Revolutionize your cancer research and treatment with the precision and efficiency of the PreciseDx™ Multimodal Comprehensive Gene Profiling (CGP).
Enable precision medicine with multimodal comprehensive genomic profiling
Driven by targeted molecular therapies and immunotherapies, precision medicine offers an individualized approach that battles cancer at its core — the genome. As new oncogenic drivers are uncovered at an unprecedented rate, a testing method that can keep pace is needed. One method meeting this challenge is comprehensive genomic profiling, or CGP.

One biomarker can make a difference
- Analyze hundreds of clinically actionable biomarkers simultaneously
- Assess DNA and RNA alterations, including SNVs, CNVs, indels, fusions, and splice variants
- Measure TMB and MSI

Maximize data from one biopsy
- Replace multiple single-gene tests or small hotspot panels with one comprehensive test
- Decrease the need to re-biopsy to obtain more data
- Reanalyze data as new biomarkers are discovered

Get results faster
- Achieve a faster turnaround time with CGP than with sequential iterative testing

Receive actionable results
- Unlock potential opportunities for molecularly matched therapy regimens
- Identify potential eligibility for matched clinical trials

Using CGP to match patients with targeted or immunotherapies has been linked to improved clinical outcomes1-5
- Increased objective response rate
- Increased overall survival
- Increased progression-free survival
Receive appropriate therapy options sooner
Illustrative example of potential patient journeys
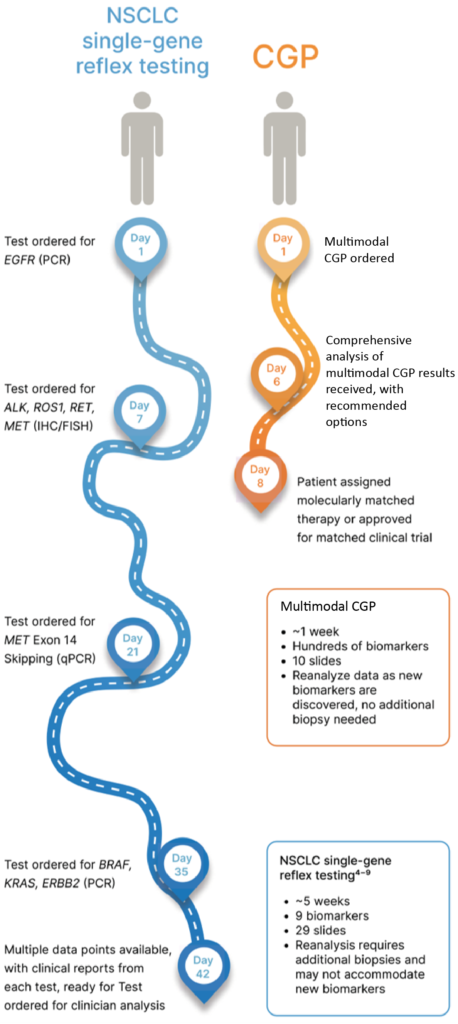
Comparison between a potential journey of a patient receiving multimodal CGP with that of a patient receiving iterative single-gene testing. Example illustrates single-gene testing based on an NSCLC patient. Test times and tissue requirements for the NSCLC example compiled from test menus offered by various medical laboratories
How to Order
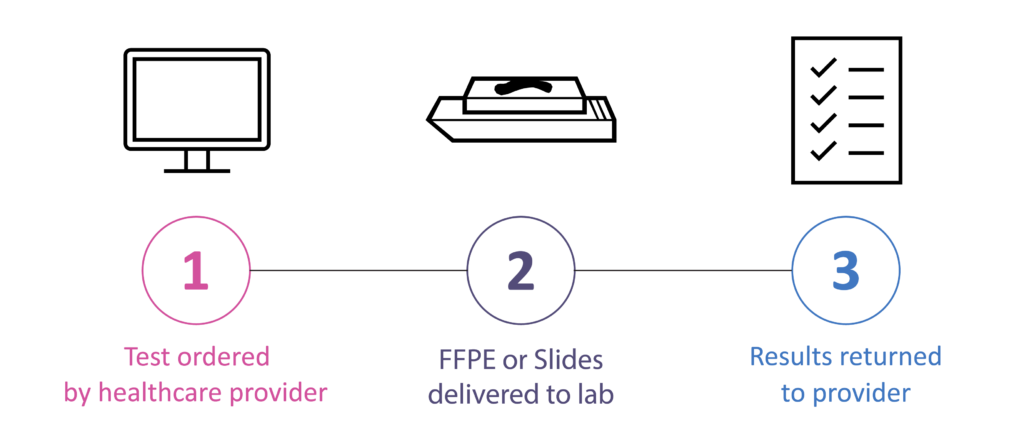
Sample Preparation Instructions
All clinical materials should be collected with approved methods to avoid contamination and cross contamination. A sterile environment must be maintained when collecting samples. Our sample preparation requirements are detailed in the table below:
| FFPE Tissue | 4 sections, each with a thickness of 10 µm |
| Ready to use DNA and RNA | ≥ 40 ng of DNA ≥ 40 ng of RNA |
Sample Transport
FFPE and DNA/RNA samples can be sent via regular mail at room temperature.
Shipping Instructions
Sample should be sent to:
AGTC Genomics Sdn Bhd (1428365-D)
J2-1, Pusat Perdagangan Bukit Jalil,
Jalan Persiaran Jalil 1,
Bukit Jalil,
57000 Kuala Lumpur,
Malaysia
References
1. Zehir A, Benayed R, Shah RH, et al. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):703-713.
2. Soumerai TE, Donoghue MTA, Bandlamudi C, et al. Clinical Utility of Prospective Molecular Characterization in Advanced Endometrial Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(23):5939-5947.
3. Gutierrez ME, Choi K, Lanman RB, et al. Genomic Profiling of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Community Settings: Gaps and Opportunities. Clin Lung Cancer. 2017;18(6):651-659.
4. Singal G, Miller PG, Agarwala V, et al. Association of Patient Characteristics and Tumor Genomics With Clinical Outcomes Among Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using a Clinicogenomic Database. JAMA. 2019;321(14):1391-1399.
5. Kato S, Kim KH, Lim HJ, et al. Real-world data from a molecular tumor board demonstrates improved outcomes with a precision N-of-One strategy. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4965.
6. Wheler JJ, Janku F, Naing A et al 2016 Cancer Therapy Directed by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling: A Single Center Study. Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 1;76(13):3690-701.
7. Hirshfield KM, Tolkunov D, Zhong H. Clinical Actionability of Comprehensive Genomic Profiling for Management of Rare or Refractory Cancers. Oncologist . 2016 Nov;21(11):1315-1325.
8. Reitsma et al., 2019. Effect of a Collaboration Between a Health Plan, Oncology Practice, and Comprehensive Genomic Profiling Company from the Payer Perspective. Journal of Managed Care & Specialty Pharmacy. 2019 Jan 11:1-10
9. Suh JH, Johnson A, Albacker L, et al. Comprehensive Genomic Profiling Facilitates Implementation of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines for Lung Cancer Biomarker Testing and Identifies Patients Who May Benefit From Enrollment in Mechanism-Driven Clinical Trials. Oncologist. 2016 Jun;21(6):684-91.
10. Drilon A, Wang L, Arcila ME, et al. Broad, Hybrid Capture-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Identifies Actionable Genomic Alterations in Lung Adenocarcinomas Otherwise Negative for Such Alterations by Other Genomic Testing Approaches. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(16):3631-3639.

